Inflation Theories - Cost-Push Inflation - What pushes inflation up?
Cost-push inflation happens when firms' costs go up. To maintain their profit margins, firms then need to put their prices up. In other words cost increases have pushed inflation up. Cost-push inflation may arise from various sources:
- Wage increases - wages are a major proportion of costs for many firms and so if wages are increasing, this may well cause cost-push inflation.
- Government - if the government changes taxes, this may push up firms' costs. This is particularly true with excise duties on fuel and oil. Changes in interest rates can also affect firms costs if they have borrowed significant amounts.
- Abroad - exchange rate changes can affect firms' costs, particularly if they import many of their raw materials. An exchange rate depreciation will increase import prices and may therefore increase firms costs.
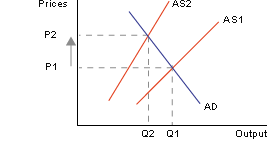
The effect of cost increases is to shift the aggregate supply to the left. As we can see from the diagram below, this pushes up prices. to the left. As we can see from the diagram below, this pushes up prices.
Intro | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5
|
|